The latest from c2w international
The scaffolding is the new career ladder
What if choosing the ‘wrong’ career path wasn’t really possible? Isabelle Kohler replaces the old metaphor of the career ladder with something more honest: a scaffolding, multidirectional and open-ended – and a space to explore for early-career researchers.
Finding the gap in electrochemical processes
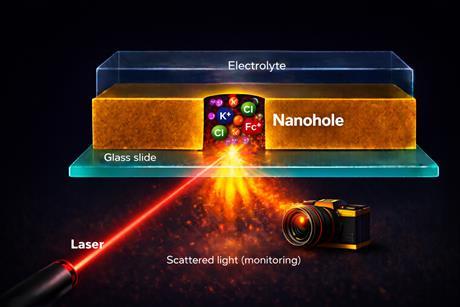
Scientists at Utrecht University have developed an optical method for visualising electrochemical processes at the nanoscale. The technique uses nanogaps and scattered light to track reactions in attolitre volumes without labelling, as the researchers demonstrate in PNAS.
Small molecule transport of copper(I) effective against cancer
For the first time, it has been possible to transport Cu⁺ through cell membranes using a small biomimetic molecule, without the aid of proteins. According to an international team in JACS, this completely unexpected development has the potential to become a potent anti-cancer strategy.
Exploring Academia with Isabelle
The scaffolding is the new career ladder
Publishing papers or creating impact?
The diversity we already have, the inclusion we still need
The virtuous circle of daring
Protecting your focus time in academia
- Previous
- Next
Nobel Prize winner Susumu Kitagawa set to speak at ECC10
‘Cross-cutting conferences are a great way to broaden your horizon’
ECC10 in Antwerp: Looking ahead
Analysing the Night Watch with top-notch chemistry
- Previous
- Next
Nobel Prize winner Susumu Kitagawa set to speak at ECC10
He was the first to discover the porosity of metal complexes, which would later become known as metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): Susumu Kitagawa is one of three Nobel Prize winners for 2025. This year, he will be the plenary speaker at the tenth EuChemS Chemistry Congress in Antwerp.
Journal retracts study on controversial lithium mine in Serbia
According to the Scientific Reports journal, the authors of a 2024 publication did not provide sufficient evidence of pollution caused by lithium exploration activities in the Jadar region of Serbia, and therefore the study has been retracted. However, some argue that the retraction comes too late, given that Rio Tinto ...
Industrial-academic collaboration sheds light on polymer analysis
Agilent Technologies, an instrument manufacturer, and the Chemometrics and Advanced Separations Team (CAST) at the Van ‘t Hoff Institute for Molecular Sciences (HIMS) at the University of Amsterdam are joining forces to gain more insight into polymers in an automated laboratory.
Protein prevents collisions on DNA ‘railway’
For DNA replication and transcription, different proteins move along DNA strands, each with its own task and speed. Researchers at Leiden University Medical Centre (LUMC) have now shown in the journal Nature that the protein CFAP20 acts as a traffic controller, preventing collisions.
Podium: Liliana Moreira Teixeira Leijten
Our members form the beating heart of our societies. Here, we regularly highlight one of them. This time, it’s NVBMB-member Liliana Moreira Teixeira Leijten.
Early-career chemists want more trust and less bureaucracy
Last summer, the inaugural Next Generation Leaders in Dutch Chemistry Summit was held at the Lorentz Centre in Leiden. During the five-day event, a group of early-career chemists (NXTGN25) from academia and industry collaborated to develop a shared vision for the future of chemistry in the Netherlands. This resulted in ...
How to stay creative in academia?
Isabelle Kohler reveals the dual system that has kept her ideas flowing: creating deliberate space for the mind to wander through low-key activities and implementing practical capture methods to store ideas when they emerge.
Move over, Matrigel – synthetic medium sets new standard
Matrigel, which is based on tumour tissue from mice, is currently the undisputed leader in the cell culture media market. However, the Nijmegen-based start-up SBMatrices is causing a stir with its fully synthetic, animal-free gel, Fybrix, which provides an equally good environment for cells and delivers consistent results.
Lumitester SMART
Why costs may rise
Engineered sampling systems ensure perfect product protection
Developing a fit-for-purpose bioprocess film
Pioneering Sensor Technology Helps Solve Biopharma Challenges
Cytiva launches first formulation system to enable end-to-end clinical and commercial manufacturing of lipid nanoparticle medicines
HOF Freeze-Thaw Unit Pharma – Next Generation
- Previous
- Next
Photo Chemistry
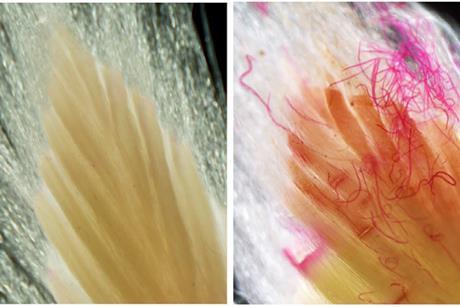
Festive fibers
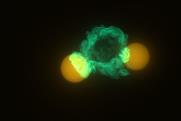
Lipids control lethal launch
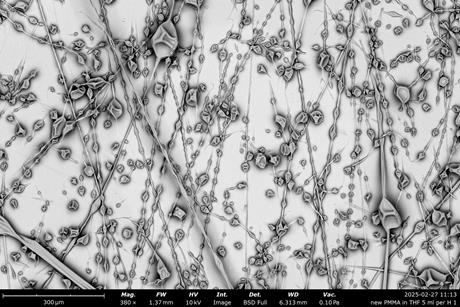
New method for controlled crystal growth
Deep-sea worm is little miss Sunshine
Gripping the green
Nasty nematodes
Stress-resistant algae
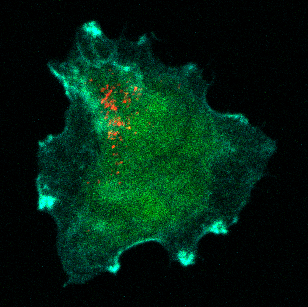
Stem cell switch
S(tea)ping against metals
Protective bubbles
- Previous
- Next